Scikit-Learn(sklearn)에서는 RandomForestClassifier, RandomForestRegressor를 이용하여 랜덤포레스트(Random Forest) 모형을 학습할 수 있다. 이번 포스팅에서는 Scikit-Learn(sklearn)을 이용하여 랜덤포레스트를 학습하는 방법을 알아본다. 랜덤포레스트는 분류 문제, 회귀 문제에 모두 적용할 수 있으므로 각각에 대해서 알아보자.
- 목차 -
1. 분류 문제(RandomForestClassifier)
2. 회귀 문제(RandomForestRegressor)
랜덤포레스트(Random Forest)에 대한 개념은 아래에 포스팅해두었으니 궁금하신 분들은 읽어보면 좋다.
24. 랜덤포레스트(Random Forest)에 대해서 알아보자
24. 랜덤포레스트(Random Forest)에 대해서 알아보자
이번 포스팅에서는 랜덤포레스트(Random Forest)에 대해서 알아보고자 한다. 랜덤포레스트(Random Forest)의 개념, 알고리즘, 여러 고려사항 및 장단점에 대해서 정리해보려고 한다. - 목차 - 1. 랜덤포레
zephyrus1111.tistory.com
1. 분류 문제(RandomForestClassifier)
랜덤포레스트를 분류 문제에 적용하기 위해 붓꽃 데이터(iris)를 이용한다. Scikit-Learn에서는 RandomForestClassifier 클래스를 이용하여 분류 모형을 학습할 수 있다.
RandomForestClassifier 클래스는 n_estimators는 개별 나무의 개수, criterion은 불순도 측도를 지정할 수 있다. 그 외 나머지 인자에 대해서는 주석을 참고하기 바라며 Scikit-Learn 개발 문서도 참고하면 좋다.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris, load_boston
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, RandomForestRegressor
iris = load_iris()
df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
df['species'] = [iris.target_names[x] for x in iris.target]
X = df.drop('species', axis=1)
y = df['species']
clf = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=50, ## 붓스트랩 샘플 개수 또는 base_estimator 개수
criterion='entropy', ## 불순도 측도
max_depth=5, ## 개별 나무의 최대 깊이
max_features='sqrt', ## 매 분리시 랜덤으로 뽑을 변수 개수
max_samples=1.0, ## 붓스트랩 샘플 비율 => 1이면 학습데이터를 모두 샘플링한다.
bootstrap=True, ## 복원 추출, False이면 비복원 추출
oob_score=True, ## Out-of-bag 데이터를 이용한 성능 계산
random_state=100
).fit(X,y)
학습된 모형에 대해서 예측과 성능 평가를 다음과 같이 할 수 있다.
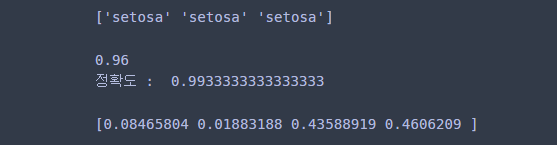
## 예측
print(clf.predict(X)[:3])
print()
## 성능 평가
print(clf.oob_score_) ## Out-of-bag 성능 평가 점수
print('정확도 : ', clf.score(X,y)) ## 테스트 성능 평가 점수(Accuracy)
print()
## 변수 중요도
print(clf.feature_importances_)
2. 회귀 문제(RandomForestRegressor)
이번에는 회귀 문제를 살펴보자. 여기서는 보스턴 집값 데이터를 이용한다. Scikit-Learn에서는 RandomForestRegressor 클래스를 이용하면 된다. 사용법은 RandomForestClassifier과 동일하다.
RandomForestClassifier에 대한 자세한 설명 Scikit-Learn 개발 문서를 참고하기 바란다.
boston = load_boston()
df = pd.DataFrame(boston.data, columns=boston.feature_names)
df['MEDV'] = boston.target
X = df.drop('MEDV', axis=1)
y = df['MEDV']
reg = RandomForestRegressor(
n_estimators=50, ## 붓스트랩 샘플 개수 또는 base_estimator 개수
criterion='squared_error', ## 불순도 측도
max_depth=4, ## 개별 나무의 최대 깊이
max_features=1/3, ## 매 분리시 랜덤으로 뽑을 변수 비율
max_samples=1.0, ## 붓스트랩 샘플 비율 => 1이면 학습데이터를 모두 샘플링한다.
bootstrap=True, ## 복원 추출, False이면 비복원 추출
oob_score=True, ## Out-of-bag 데이터를 이용한 성능 계산
random_state=100
).fit(X,y)
모형을 학습했다면 이를 평가할 수 있다.
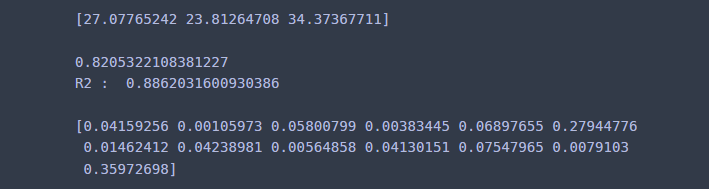
## 예측
print(reg.predict(X)[:3])
print()
## 성능 평가
print(reg.oob_score_) ## Out-of-bag 성능 평가 점수
print('R2 : ', reg.score(X,y)) ## 테스트 성능 평가 점수(Accuracy)
print()
## 변수 중요도
print(reg.feature_importances_)





댓글